How Is Behavior Therapy Different From Psychoanalysis?

Our minds are a work of miracle and mystery, and sometimes, we need guidance to help us make sense of all the twists and turns that our minds go through. Some people find help in the form of self-reflection and meditation, while others find themselves seeking therapy to help them make sense of it all.
Out of all, the two therapy approaches that work well in helping us understand our minds are behavioral therapy and psychoanalysis. These two guides, if you will, offer different approaches to understanding and improving our mental well-being, but they work effortlessly. While each of them has the same goal, more or less, the way they help can differ.
So, how can we know which approach works best for us? Are these two therapy approaches the same? How is behavioral therapy different from psychoanalysis when they both aim for the same thing?
Well, let’s take a stroll through the corridors of our minds and discover what sets these two therapy approaches apart. Keep reading to know in what ways psychoanalysis and behavioral therapy (CBT) differ from each other.
Behavioral Therapy: What is it & How it Works?
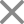
Your mind is a canvas, and behavioral therapy is the brush. This therapy approach focuses on observable behaviors and aims to change your negative patterns. Therapists work with you to identify and replace harmful behaviors with healthier and positive ones. It’s all about reshaping habits and thoughts to create a more positive and fulfilling life.
History of Behavioral Therapy:
If we look into the past of Behavior therapy, it was introduced by Russain psychologist, Ivan Pavlov, in between the 1920s and 1930s. His study focused on classical conditioning where two stimuli are connected to find a new response. One of the famous experiments by Pavlov included a method where dogs salivate as soon as the bell rings. This showed that dogs showed a particular response as soon as the bell rang.
Behavioral therapy can be better used to address these issues;
- Substance abuse
- Insomnia
- Stress
- Depression
- Anxiety disorders
- Obsessive compulsive disorder
- Bipolar disorder
- Schizophrenia
- Personality disorder
- Psychotic disorders
Some common techniques that behavioral therapies engage in to help your mind can include;
- Exposure Therapy
- Cognitive Restructuring
- Behavioral Activation
- Systematic Desensitization
Components Of Behavior Therapy
1. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): The therapist tries to find out unhealthy thoughts patterns that a person is going through and what is the impact of these thoughts on a person. Once understood, the therapist tries to help the person replacing their negative thoughts and imbibe healthier ones back in life.
2. Aversion Therapy: Aversion therapy is meant to provide a person dealing with addiction or any other unwanted habit which disrupts the lifestyle. Behaviors like alcoholism, gaming, violence, anger, smoking, gambling, self injuries, etc. could be reverted with this behavior therapy.
3. Dialectical Therapy (DBT): DBT is meant to structure the immediate environment, enhance motivation and capabilities. This therapy works most appropriately with patients dealing with borderline personality disorder.
4. Systematic Desensitization: A type of gradual exposure therapy, it mainly focuses on gradual exposure to the fear while also maintaining relaxation, safety and calm.
Psychoanalysis: What is it & How it Works
Now, coming on to psychoanalysis. It’s an approach pioneered by Sigmund Freud. Psychoanalysis is like digging into the layers of your mind to understand where your behaviors, emotions, and thoughts come from. Through techniques like free association and dream analysis, psychoanalytic therapists can help bring repressed issues to the surface, offering insights that help you heal and grow.
History of Psychoanalysis :
Also considered as the first form of psychotherapy, many other theorists like Carl Jung, Anna Freud and Erik Erikson worked on the same section for quite a long time. Human development was taken into consideration while stressing the growth throughout the lifecycle.
Psychoanalysis can be used to better understand and treat conditions such as;
- Depression
- Low self-esteem
- Emotional traumas
- Relationship problems, and more
- Panic attack
- Hypersensitivity
- Workaholism
Some common psychoanalytic techniques that you can engage in for your mind can include;
1. Dream Analysis:
Freud believed that dreams act as a doorway to get into the unconscious state and understand what happened in the previous stages. He also believed that dreams also have sexual meaning hidden within them.
2. Free Association :
In this strategy, the therapist reads a list of words and the person is required to answer anything that comes to their mind. It helps the therapist to go through the memories stored in the unconscious mind.
3. Transference:
This therapy is meant to ‘transfer’ the feelings of a person towards a key figure, be it from their past or present. It helps in bridging the gap between unconscious and conscious in a better manner.
4. Childhood Experiences Exploration
How is Behavioral Therapy Different From Psychoanalysis?
Now that you know the basic workings of each therapy approach, let’s dive into understanding the differences between behavioral therapy or CBT and psychoanalysis.
1. Their Focus
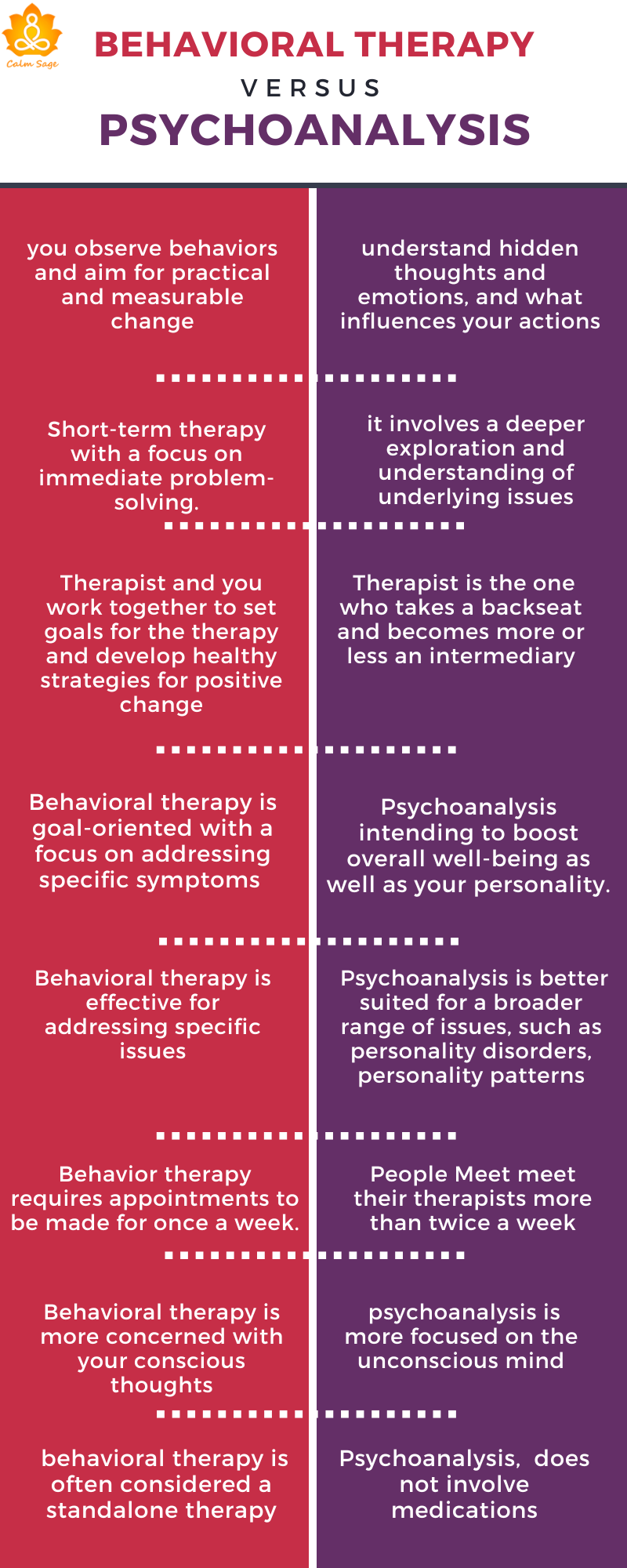
In behavioral therapy, you observe behaviors and aim for practical and measurable change. In psychoanalysis, you delve into the unconscious mind, seeking to figure out and understand hidden thoughts and emotions, and what influences your actions.
2. Their Time Frame
Behavioral therapy is generally short-term therapy with a focus on immediate problem-solving. But, on the other hand, psychoanalysis takes long therapy sessions as it involves a deeper exploration and understanding of underlying issues over immediate and superficial problem-solving.
3. The Role of Therapist
In behavioral therapy, the therapist and you work together to set goals for the therapy and develop healthy strategies for positive change. In psychoanalysis, the therapist is the one who takes a backseat and becomes more or less an intermediary, helping you gain insights into your unconscious mind.
4. Their Orientation
Behavioral therapy is goal-oriented with a focus on addressing specific symptoms and problems. On the other hand, psychoanalysis emphasizes self-reflection, self-discovery, and understanding deep-rooted patterns, intending to boost overall well-being as well as your personality.
5. Their Application
Behavioral therapy is effective for addressing specific issues such as anxiety disorders, phobias, and obsessive-compulsive disorders. Psychoanalysis, on the other hand, is better suited for a broader range of issues, such as personality disorders, personality patterns, complex trauma, and chronic relationship issues.
6. Their Emphasis on Conscious and Unconscious Mind
Behavioral therapy is more concerned with your conscious thoughts, behaviors, and other environmental factors that influence your behaviors, whereas psychoanalysis is more focused on the unconscious mind and the influence of early life experiences on current thoughts and behaviors.
7. Medication Management
When we talk about medication management in therapy, behavioral therapy is often considered a standalone therapy, but it can be used as a complementary therapy with medication management. When it comes to psychoanalysis, it can be safe to say that this approach does not involve medications, as the focus of this therapy is on talk therapy and self-exploration.
How to Choose Between The Two Approaches?
Choosing between CBT or behavioral therapy and psychoanalysis is like selecting the right candidate for your treatment.
Because of their unique and candid approach, you need to consider these factors;
- If you’re seeking practical and more goal-oriented solutions, then consider behavioral therapy your go-to therapy approach.
- If you’re seeking, or you’re curious about the root causes of your thoughts, behaviors, and emotions, then the psychoanalysis therapy approach could be better suited for you.
- You can choose psychoanalysis if you want to learn more about your past trauma and how it impacts your current self. Keep in mind that psychoanalysis isn’t short-term therapy, so you should be ready to commit to the therapy and healing process.
- CBT or behavioral therapy can be good if you’re seeking help for problems such as self-harm, low self-esteem, or negative thinking. Behavioral therapy approaches are more action-oriented, so pick this approach when you are ready to work outside of therapy sessions as well.
Wrapping Up…
When it comes to mental health, both behavioral therapy and psychoanalysis offer valuable routes for self-discovery and self-improvement. Whether you opt for the gentle strokes of behavioral therapy or the deeper digging into your subconscious with psychoanalysis, the end goal is the same: the desire for a healthier and more balanced mind.
So, whichever approach you pick, remember to go into it with an open heart, a curious mind, and the knowledge that no matter what approach you have chosen, it’s a step toward a better understanding of yourself and the intricacies of your mind.
Did you find this article interesting? Were we able to help you understand the differences between behavioral therapy and psychoanalysis? Let us know your thoughts and views about the article in the comments box below.
Take Care!