Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT)- How It Works

We all wake up each morning with one thought common in all of our head, and that is making our ‘Life worth living.’
Don’t we?
Well, while some of us manage to achieve it and live by it, many are continually striving for the same. Why? Because each one of us is fighting a different fight! And for some of us, these challenges are too overwhelming to deal with. And that’s okay!!! What’s not okay here is- letting these challenges take a toll on our physical and mental health. To help you with the same, there exists a fantastic therapy, known as Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT Therapy).
Dialectical Behavior Therapy was propounded by Dr Marsha Linehan, inspired by her journey of mental health recovery (making it more realistic). DBT Therapy is a form of talk therapy to help others modify existing behavior, regulating emotions, and encouraging them to solve the problems of life. The cherry on the top is it is found to be effective in the long run.
Now let us understand DBT Therapy in-depth.
The theory behind Dialectical Behavior Therapy
DBT works on three major theoretical frameworks. This includes:
Dialectics: DBT works on a philosophical process called dialectics (hence the name dialectical). This process of dialectics is based on the concept that everything around us is composed of opposites, and change will only occur if there is a dialogue between opposing forces. Ideally, dialectics is based on three basic assumptions:
- Everything is interconnected
Opposites can be integrated to form a closer approximation of the truth - Change is inevitable and constant
Validation: The second focus of this DBT is the process of validation. Here the therapist validates or gives a sense to the person’s action within the context of their personal experience. This brings more cooperation and reduces the distress of the person.
Mindfulness: DBT draws techniques of Zen Buddhism that allows an individual to be in the present moment. Mindfulness will enable people in therapy to assess situations calmly on the one hand and let them use stock of their current experience, evaluate facts, and focus on one thing at a time.
Goals of Dialectical Behavior Therapy
The objectives of DBT therapy are generally stage oriented. However, the critical goals of DBT are:
- Bring stability in the life of an individual
- Help individual get control over the problematic area
- Allow people to accept and work on their emotions instead of putting them at bay
- Promote happiness by enhancing the quality of life
- Let the individual achieve and maintain an ongoing capacity for success and happiness.
Components of Dialectical Behavior Therapy
There are five key components of DBT Therapy that makes it a perfect treatment approach for various mental health conditions. These five core components are:
- Structuring the immediate environment. DBT ensures that an individual learns positive and adaptive behaviour which can be enforced across all environmental settings of their life.
- Motivational enhancement. DBT focuses on reducing behaviour that might hurt the quality of life. Along with this, it actively works on problematic behaviour.
- Capability enhancement. With the idea that we have all that we need, DBT helps in developing the existing skills intensively and effectively.
- Capability and motivational enhancement of therapists. The target population of DBT varies widely; this allows the therapists to gain insights, receive supervision, and be motivated to prevent extreme situations in which an individual can place himself.
- What is learnt through DBT (DBT skills) can be generalized in almost all settings; in fact, the therapist and team of consultation ensure that the learned skills are applied in all areas of life.
Stages of Dialectical Behavior Therapy
DBT therapy works on a systematically and comprehensively designed model. It works on a 4-stage model that aims at addressing all concerns of a given problem.
Pre-Treatment (4-6 weeks)
Goals: To identify the goals of therapy. Enhance motivation and commitment in the client.
Stage 1 (Commitment, Stability, & Safety)
Goals: The goals at this stage are working on interfering behaviors like-
Life-threatening, Therapy- interfering, and quality-of-life behaviors.
Stage 2 (Symptom Reduction)
Goals: Dealing directly with the symptoms of the problem being faced by the client that are interfering in the current life functioning. This may include symptoms of trauma, eating, mood, or anxiety disorder, or any other mental health condition that is currently being addressed.
Stage 3 (R.E.A.C.H.)
Goals: The goal of this therapy is to Regulate Emotions through Acceptance and Change (R.E.A.C.H) with a special focus on relationship difficulties, low self-esteem, and problem-solving.
To work on these goals, specific interventions are undertaken in DBT therapy. These modes of treatment include:
- Individual Therapy (1hr/week): These hour-long sessions focus on talking about those aspects that you want to work on with your therapist. So that you can build on the necessary skills to sail through life challenges.
- Group Skills Training (2.5hr/week): These sessions are similar to group therapy sessions. It allows you to practice each skill and talk through scenarios with other people in the group.
- Therapist Consultation Team (1-1.5 hr/wk): The aim of the consultation team to solve all your queries regarding DBT Therapy. This team of 3-8 people (each with a different role to offer) helps you manage your life effectively in all situations.
- Phone Caching (As needed): Often, therapists offer phone coaching to provide extra support. They guide you to put your DBT skills to use.
When Does Dialectical Behavior Therapy Work?
Ideally designed for the treatment of suicidal behavior and borderline personality issues now it is adapted for other mental health conditions as well. Currently, there are many areas in which DBT therapy has been found to work amazingly well. This includes:
- Regulation of moods
- Bringing stability in behavior, relationship, thinking pattern.
- Boosting self-esteem
- Fewer anger episodes
- Improved social functioning
- Controlling Binge eating and symptoms of ADHD
- Dealing with PTSD
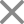
Modules of Dialectical Behavior Therapy
DBT therapy teaches people to change their behavior effectively by using the following four strategies viz.,
- Core Mindfulness: This is perhaps the most integral part of DBT therapy and sets this therapy apart. It teaches individual core mindfulness skills “what” that is to observe, to describe, and to participate. Along with this, it also works on the “how” skills that are non-judgmentally, effectively, and one-mindfully. It is taught with the idea to help the person find calmness.
- Interpersonal Effectiveness: This strategy of DBT therapy helps an individual to interact with others and work on their relationships effectively. The techniques are similar to assertiveness and interpersonal problem-solving approaches, teaching to listen and communicate effectively.
- Distress Intolerance: While many therapeutic approaches focus on eradicating distressing events and circumstances, little focus is given to accepting, evaluating meaning, and tolerating distress. DBT therapy, in contrast, focuses on these aspects of distress. It is achieved by developing skills in an individual to endure and survive crises by accepting the current moment that life has to offer. The essential four skills are self-soothing, distraction, working on the moment, and thinking of good and bad of not tolerating distress.
- Emotion Regulation: Emotion regulation strategy focuses on helping the individual develop insight into one’s emotions. It teaches the identification and labeling of emotions by increasing mindfulness of the current emotions. This further allows us to embrace positive emotional experiences in life.
Image Source: Psychiatrictimes.com
Effectiveness of Dialectical Behavior Therapy
Multiple studies have time and again reflected the efficiency of DBT therapy. Some of its vital effectiveness are:
- A survey conducted by Linehan et al. is found to reduce attempts of suicide.
- Independent studies on DBT therapy found that it decreases instances of self-harming behaviors as compared to other treatments.
- Bohus et al. in a study found that people receiving DBT therapy show a better, steady, and remarkable recovery.
Limitations of Dialectical Behavior Therapy
Being a comparatively new approach to talking therapy DBT has its limitations like-
- The samples of DBT therapy research included small sample sizes. Therefore, it has more scope of being researched.
- DBT therapy is effective, but it uses a detailed manual and calls forth intensive training and implementation of the same.
Now that you know everything about Dialectical Behaviour Therapy, it is time for you to think it over and see if you or a loved one should go for it. Trust me, going for therapies is a healthier option over suffering any day. So, either be your guiding light or someone else’s by promoting wellness.
More Power to You and Your Loved Ones
You May Like these Also:
Do’s and Don’ts for Recovering From Eating Disorders
Top 10 Movies About Psychological Disorders
Avoiding These Vitamins Can Trouble Mental Health. Start Them Today!